MinIMU-9 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass
We have ✅ 3 available of the PL-1265 in our Sydney warehouse.
This board has been replaced by the newer MinIMU-9 v2 L3GD20 and LSM303DLHC carrier, which offers improved magnetic sensing resolution, a wider acceleration measurement range, and gyro measurements that are more resistant to audio noise and vibrations. The new version is also 25% smaller than the original. The MinIMU-9 v2 is pin-compatible with the previous version, but the mounting hole location has changed, and the new ICs have different I²C addresses and configuration registers, so code written to interface with the MinIMU-9 will need to be modified to work with the MinIMU-9 v2.
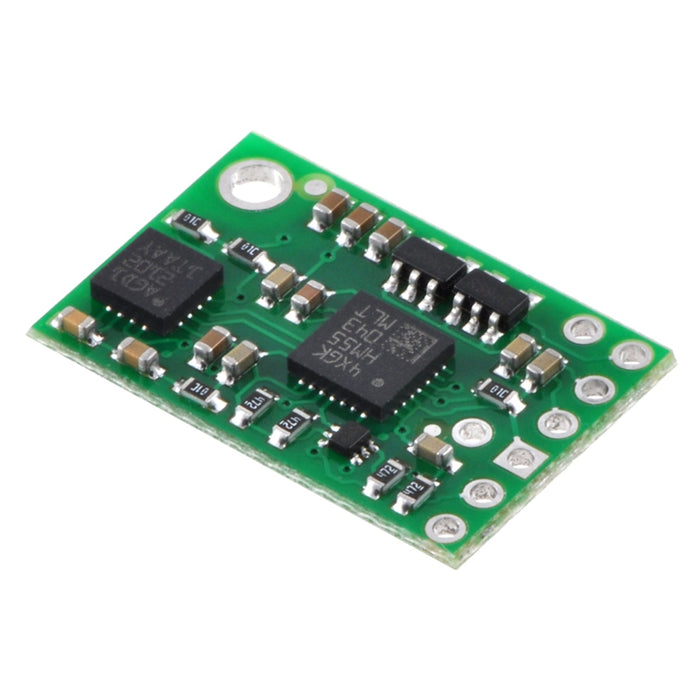
The Pololu MinIMU-9 is a compact (0.9″ × 0.6″ × 0.1″) board that combines ST’s L3G4200D 3-axis gyroscope and LSM303DLM 3-axis accelerometer and 3-axis magnetometer to form an inertial measurement unit (IMU); we therefore recommend careful reading of the L3G4200D datasheet (1MB pdf) and the LSM303DLM datasheet (519k pdf) before using this product. These sensors are great ICs, but their small packages make them difficult for the typical student or hobbyist to use. They also operate on multiple voltage supplies that make interfacing with 3.3 or 5 V systems challenging. The MinIMU-9 addresses these issues by incorporating additional electronics, including two voltage regulators and a level-shifting circuit, while keeping the overall size as compact as possible. The board ships fully populated with its SMD components, including the L3G4200D and LSM303, as shown in the product picture.
The Pololu MinIMU-9 is a compact (0.9″ × 0.6″ × 0.1″) board that combines ST’s L3G4200D 3-axis gyroscope and LSM303DLM 3-axis accelerometer and 3-axis magnetometer to form an inertial measurement unit (IMU); we therefore recommend careful reading of the L3G4200D datasheet (1MB pdf) and the LSM303DLM datasheet (519k pdf) before using this product. These sensors are great ICs, but their small packages make them difficult for the typical student or hobbyist to use. They also operate on multiple voltage supplies that make interfacing with 3.3 or 5 V systems challenging. The MinIMU-9 addresses these issues by incorporating additional electronics, including two voltage regulators and a level-shifting circuit, while keeping the overall size as compact as possible. The board ships fully populated with its SMD components, including the L3G4200D and LSM303, as shown in the product picture.
The L3G4200D and the LSM303 have many configurable options, including dynamically selectable sensitivities for the gyro, accelerometer, and magnetometer, as well as a choice of output data rates for each sensor. The two ICs can be accessed through a shared I²C/TWI interface, allowing all three sensors to be addressed individually via a single clock line and a single data line. The nine independent rotation, acceleration, and magnetic readings (sometimes called 9DOF) provide all the data needed to make an attitude and heading reference system (AHRS). With an appropriate algorithm, a microcontroller or computer can use the data to calculate the orientation of the MinIMU-9 board; the gyro can be used to very accurately track rotation on a short timescale, while the accelerometer and compass can help compensate for gyro drift over time by providing an absolute frame of reference. The respective axes of the two chips are aligned on the board to facilitate these sensor fusion calculations. (For an example of such a system using an Arduino, see the picture below and the Sample Code section at the bottom of this page.)
The MinIMU-9 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass appears in the following collections:
SKU PL-1265
by Little Bird